Designed to enable computer clients to save power, MIMO power save mode is also referred to as spatial multiplexing power save (SMPS) mode. It keeps one antenna in an idle receive state to save power.
MIMO Power Save Mode
The four main MIMO power save modes include:
Dynamic SMPS
In this mode, the client enables only a single antenna to stay active. The client wakes the antenna or radio in sleeping mode after the access point (AP) sends an RTS packet transmission request, but prior to relaying MIMO packets.
Auto SMPS (default mode)
This is the default mode. It automatically selects the proper SMPS mode based on prevailing conditions.
No SMPS
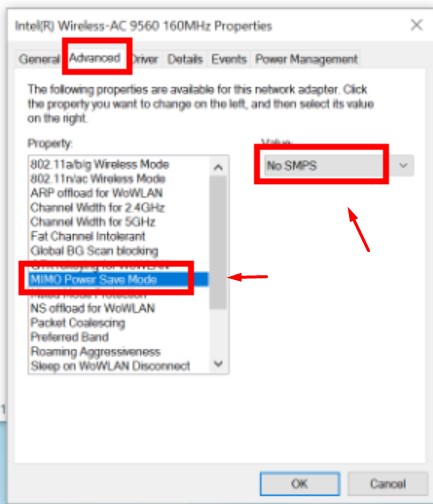
In this mode, the client ensures that all antennas remain active, and the access point transmits MIMO packets to the client.
Static SMPS
In this mode, the client enables only a single antenna to stay active, and the access point cannot transmit MIMO packets to the client.
Some traditional access points do not support the SMPS mode due to compatibility problems, resulting in multiple quality-related issues, such as low throughput. If experiencing this problem, you need to alter settings to No SMPS.
MIMO Power Saving Mode for Wireless Adapters
Wireless Adapter Settings available under Power Options have a Power Saving Mode feature. You can use this feature to control your wireless adapters’ power-saving mode.
The more you boost your computer’s power savings, the lower the performance and strength of your wireless network. However, increasing the power saving improves your PC’s battery life.
Ad-hoc Quality of Service (QoS) Mode
Ad-hoc network’s QoS control prioritizes access point traffic over packets from a wireless local area network (WLAN) according to traffic categorization. Wireless Alliances’ (WFA) QoS certification is known as wireless or Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM).
The wireless adapter uses WMM, when activated or enabled, to support queuing and priority tagging capabilities under wireless networks. The WMM feature is disabled by default and isn’t available in Windows 10.
Global BG Scan Blocking
The wireless adapter, by default, runs periodic scans for other access points (AP) available on the same network. When using software applications prone to short network connectivity interruptions, disable this feature. Settings options include:
- Never (default) – conducts periodic scans for other APs available on the network.
- Always – doesn’t conduct periodic scans for other APs available on the network.
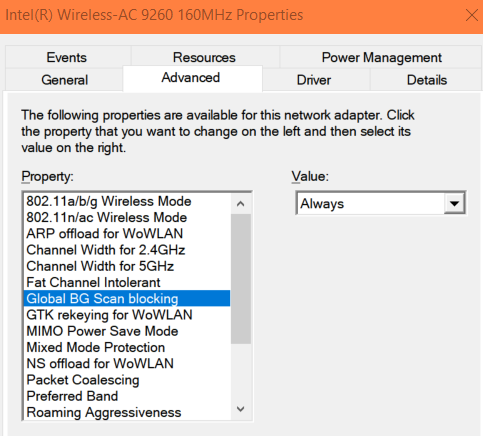
- On Good RSSI – only conducts periodic scans for other APs available when the signal strength of the existing access point (AP) becomes low.
Note that this feature isn’t recommended if you’re usually mobile on your work days.
Preferred Band
Frequency bands help reduce noise or interference in environments with multiple devices that use radiation technology, such as access points, wireless telephones, client devices, or even microwave ovens.
Choose the 5GHz band instead of the 2.4GHz band or the latter over the former. Options include:
- Prefer 2.4GHz band
- No Preference (default)
- Prefer 5GHz band
Transmit Power
The lowest transmit power level is the optimal setting and still meets communication standard quality. It enables the highest number of wireless devices to function in dense areas.
The setting ensures that radiating devices within the same radio spectrum experience minimal interference. Radio coverage reduces as you decrease the level of transmit power. Settings options include:
- Highest (default) – Maximum transmit power adapter level increases range and performance in environments with a few radio devices.
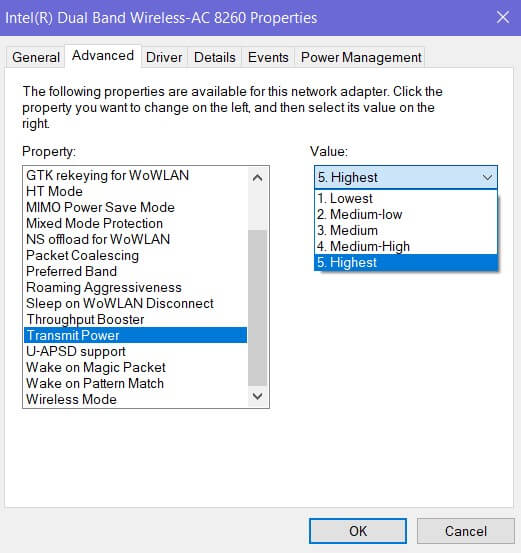
- Medium, Medium-low, or medium-high – choose the right setting based on your country’s requirements.
- Lowest – the lowest transmit power adapter level increases or confines coverage area. In environments with high traffic, reduce the coverage area to prevent interference with other radio devices or congestion and enhance general quality of transmission. Enable the Device to Device (ad-hoc) or Network (Infrastructure) mode to use this setting.
U-APSD Support
Built to reduce power consumption on low periodic traffic modes sensitive to latency, such as VoIP, U-APSD is also known as WMM-PS or WMM-Power Saver. The wireless capability may experience interoperability (IOT) issues with particular access points linked to lower RX throughput.
Setting options for this feature include:
- Enabled
- Disabled (default)
Mixed Mode Protection
With mixed mode protection, you can prevent data collisions in mixed 802.11g and 802.11b network settings. In environments where clients may be unable to communicate, use Request to Send/Clear to relay (RTS/CTS).
Increase throughput using CTS-to-self in environments where clients can communicate. Setting options include:
- RTS/CTS Enabled (default)
- CTS-to-self Enabled
This setting isn’t available when you activate the 802.11n mode.
NS Offloading for WoWLAN
NS offload setting enables network adapters to respond to requests for Neighbor Discovery Neighbor Solicitation with a Neighbor Advertisement while the computer is asleep. This feature functions only when the driver and hardware support NS offload. Setting options include:
- Disabled
- Enabled (default)
Roaming Aggressiveness
Use this setting to reduce or increase the wireless adapter’s signal strength when it begins to scan for other access point candidates. Setting options work differently based on the network environment, with some performing better than others.
If changes to your wireless adapter do not make any improvement, go back to the default setting (Medium). Setting options include:
- Medium-Low
- Medium-High
- Medium (default) – recommended option.
- Lowest – when signal strength of an existing access point is extremely low, the wireless adapter initiates a scan for another AP.
- Highest – when the signal strength of the existing access point is strong enough, the wireless adapter initiates a scan of another AP.
Throughput Booster or Improvement
Packet bursting improves the transmit throughput. The client holds air medium longer than it usually does to relay data to access points (AP) when throughput booster is enabled, and the wireless adapter has collected enough data.
The data upload throughput from the client to the access point improves, effectively enhancing upstream benchmarks or large file uploads. Setting options include:
- Disabled (default)
- Enabled
Enabling the throughput booster of a single client reduces the throughput of other clients within the same network. This is because only one device can send data while this feature is enabled in a wireless network.
Fat Channel Intolerant
Wireless adapters communicate to nearby networks when this setting is enabled, announcing that they do not tolerate 40MHz channels within the 2.4 GHz band. The adapter does not communicate this information when the feature is disabled. Setting options include:
- Disabled (default)
- Enabled
Conclusion
The MIMO Power Save Mode is also referred to as spatial multiplexing power save (SMPS) mode. It makes one antenna idle to help save power. The power-saving mode has many features you can enable or disable to improve the performance of your wireless network adapter.
With options ranging from throughput booster to global BG scan blocking, you can set various options under this feature to improve the performance of your wireless adapter while saving power.

